Pain is a highly individualized experience, and wellness strategies for comfort and support vary from person to person. While some individuals explore pharmaceutical pain management, others look into movement, relaxation, or hydration-based approaches as part of their overall wellness journey. Researchers report that 50.2 million (20.5 percent) U.S. adults experience chronic pain based on analysis of the new NHIS data.
Exploring Non-Pharmaceutical Pain Management Approaches
Some individuals explore wellness-based approaches to pain management that do not involve pharmaceuticals. These may include:
- Cold or heat therapy
- Stretching, movement, and body awareness practices
- Breathwork, meditation, and relaxation techniques
- Physical therapy, massage, or acupuncture-based approaches
Can Long-Term Pain Management Be Achieved?
Pain experiences are unique to each individual, and managing discomfort is often a multi-faceted process. While some individuals find long-term relief when contributing factors are addressed holistically, pain management strategies vary from person to person.
Some wellness practitioners explore factors such as circulation, lymphatic flow, environmental influences, and overall balance when considering holistic wellness approaches. Individuals interested in pain management strategies may benefit from working with a qualified healthcare provider to explore options that best support their well-being.
Exploring Wellness Approaches for Post-Surgical Recovery
Pain is a common part of the recovery process, and individuals often seek different approaches to support their comfort during healing. Many individuals explore a variety of wellness approaches, including movement, relaxation techniques, and hydration, to support post-surgical recovery.
Adequate rest, gradual movement, stress management, and hydration are often considered important factors in supporting the body during recovery. Exploring wellness-based approaches alongside guidance from a qualified healthcare provider may help individuals find strategies that best support their healing journey.
Exploring Non-Pharmaceutical Approaches to Comfort and Wellness
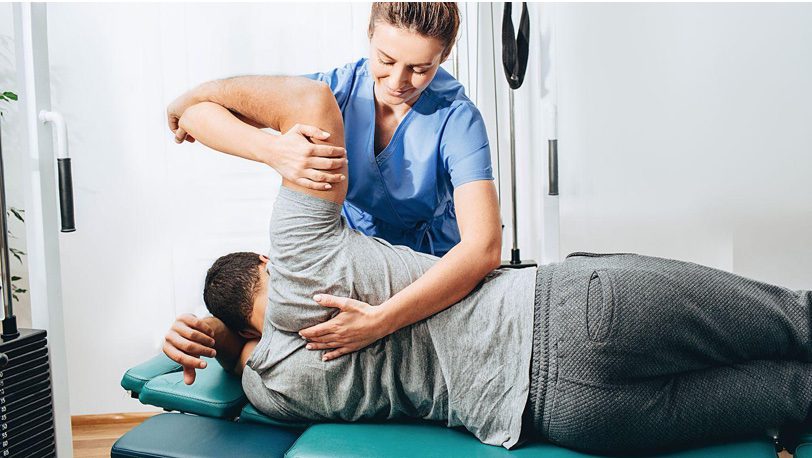

Many individuals explore various approaches to support comfort without medications. Some wellness-based methods include gentle movement, yoga, tai chi, acupuncture, stress management, and physical therapy.
According to the American Physical Therapy Association, physical therapists teach self-management skills that may help individuals with arthritis improve strength, mobility, and flexibility. This may also include guidance on movement-based strategies that align with a person’s individual wellness goals.
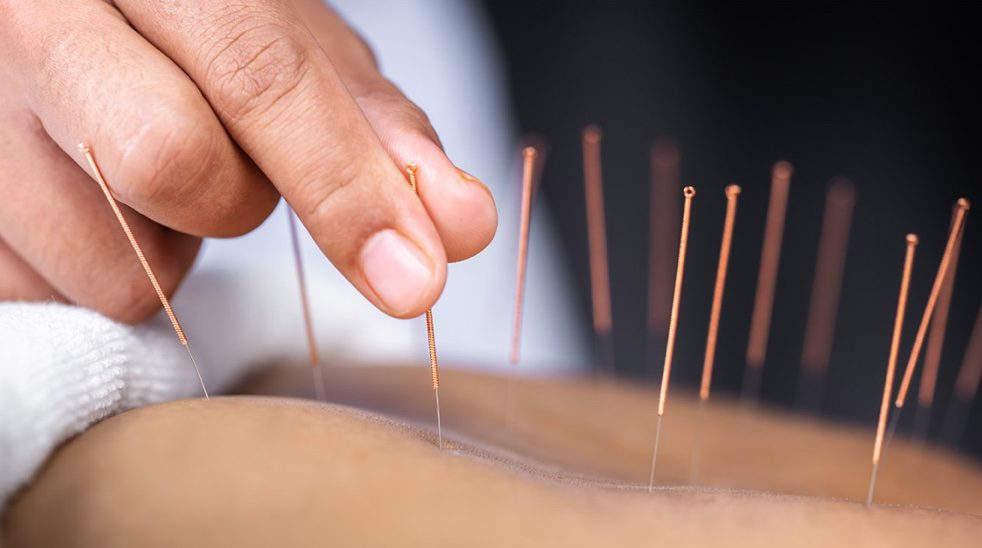
Acupuncture is a wellness practice that some individuals explore as part of their holistic approach to well-being. In traditional practice, fine needles are placed in specific areas to promote balance. Some research explores how acupuncture may influence the body’s response to external stimuli.

Understanding Pain & Circulation
Circulation plays a key role in overall wellness. Some individuals find that movement, hydration, and other wellness practices may contribute to supporting circulation.
Considering Wellness Approaches for Comfort
Supporting daily wellness may involve hydration, nutrient-rich foods, relaxation techniques, and regular movement. Each individual’s wellness experience is unique, and exploring different approaches with the guidance of a qualified provider can be beneficial.
📌 Disclaimer: Doctor Me and You focuses exclusively on wellness education and does not provide medical services. We are not state-licensed physicians and do not diagnose, treat, or prescribe medications for any condition. Information shared during consultations or in communications is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider for medical concerns.
